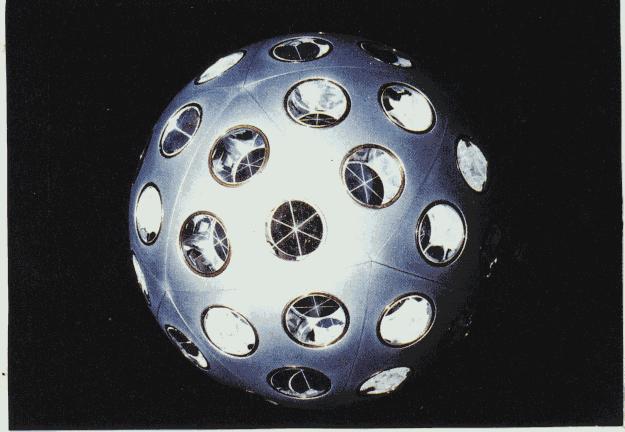

The LAGEOS program aim is to measure the Earth gravity potential. This is very simply done by observing an artificial satellite orbiting in the Earth gravity field. If the Earth were simply homogeneous and spherical, anny satellite would orbit around it along a stable ellipse. Since this is not the case, the orbit is perturbated, and the satellite displacement looks like if it were "rolling on a bumpy surface around the Earth". This surface is the equipotential of the gravity field potentiel at the altitude of the satellite. By simply measuring the distance between ground stations and the satellite (usually by means of lasers reflected by mirrors dispatched on the satellite surface), one can determine the shape of this equipotential surface.
A bunch of satellites were launched since the mid seventies to achieve this task :